Oct 11,2025
Oct 11,2025Executive Summary
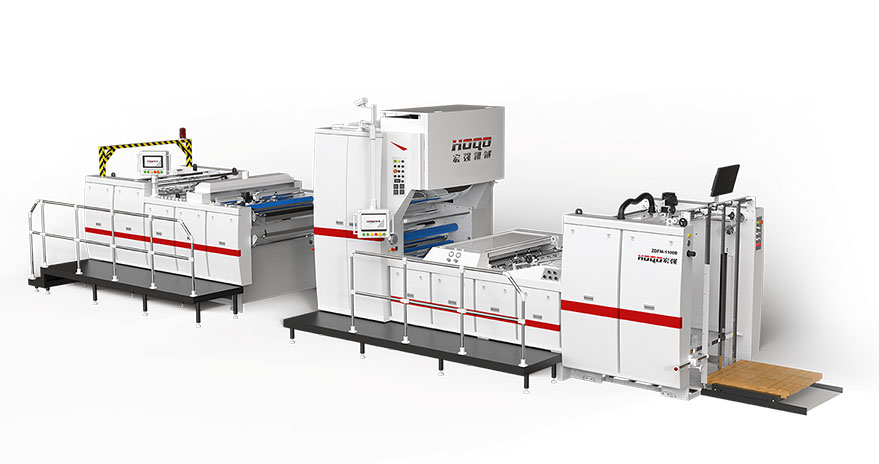
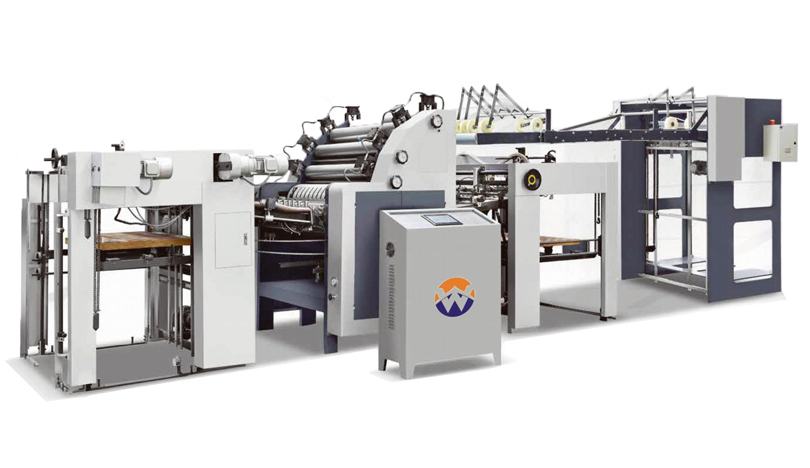
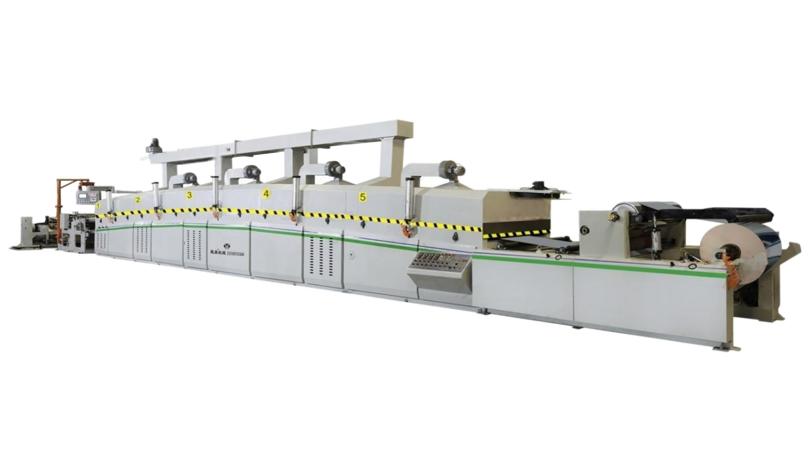
The global market for Automatic Thermal Film Laminators is a dynamic and critical segment within the broader printing and packaging finishing industry. These machines, essential for enhancing the durability, aesthetic appeal, and professionalism of printed materials, represent a significant investment for businesses of all sizes. Navigating this market requires a deep understanding of technical specifications, operational needs, supplier capabilities, and post-purchase support. This comprehensive guide is designed to serve as an authoritative resource for international buyers at various levels. It provides a structured, multi-dimensional framework to inform decision-making throughout the entire procurement lifecycle: pre-purchase, during purchase, and post-purchase. By dissecting the requirements of different buyer tiers and outlining critical considerations at each stage, this guide aims to empower buyers to make strategic, cost-effective, and future-proof investments. The analysis will subtly reference the approach of industry players like Hongqiang, which exemplifies a focus on robust engineering and practical solutions for specific market segments.
Section 1: Understanding the Buyer Landscape – A Tiered Approach
The first step in a successful procurement journey is self-assessment. Buyers are not a monolith; their needs, budgets, and expectations vary dramatically. We categorize buyers into three primary tiers.
1.1 Tier 1: Small to Medium-sized Enterprises (SMEs) / Print Shops
-
Profile: Typically owner-operated or with a small team. They handle diverse, short-run jobs (business cards, brochures, flyers, menus). Budget is often a primary constraint.
-
Key Needs:
-
Affordability: Seeking the best value for money without excessive upfront cost.
-
Ease of Use: Minimal training requirements; intuitive controls.
-
Versatility: Ability to handle a wide range of substrates (paper, cardstock) and film types (gloss, matte, soft-touch).
-
Space Efficiency: Compact footprint is crucial for limited workspace.
-
Reliability: Low downtime is essential for business continuity.
-
-
Primary Concerns: Over-investing in underutilized features; hidden costs of maintenance; complexity leading to operational bottlenecks.
1.2 Tier 2: Large Commercial Printers & Packaging Converters
-
Profile: High-volume operations with dedicated finishing departments. They serve corporate clients, publishers, and require high throughput and consistent quality.
-
Key Needs:
-
Productivity & Speed: High laminating speeds (meters/minute) and quick job changeover times.
-
Durability & Uptime: Industrial-grade construction capable of 24/7 operation with minimal maintenance interruptions.
-
Advanced Features: Precision temperature control, automatic pressure adjustment, compatibility with thick substrates and specialty films (e.g., holographic, anti-scratch).
-
Integration: Seamless workflow integration with existing pre-press and printing systems (e.g., CIP4/JDF compatibility).
-
Quality Control: Consistent, bubble-free, and misalignment-free results across long runs.
-
-
Primary Concerns: Production bottlenecks; quality inconsistencies leading to waste and reprints; total cost of ownership (TCO) over the machine's lifespan.
1.3 Tier 3: Specialized Service Bureaus & High-End Finishing Houses
-
Profile: Focus on premium, value-added finishing for luxury packaging, fine art reproductions, photographic prints, and security documents.
-
Key Needs:
-
Ultimate Quality & Precision: Ability to handle delicate and expensive materials without damage. Superior registration accuracy.
-
Specialized Capabilities: Support for cold thermal fusion techniques, low-temperature films, textured finishes, and encapsulation.
-
Customization: Flexibility for custom configurations to meet unique client demands.
-
Technical Support: Access to highly trained service engineers with specialized knowledge.
-
-
Primary Concerns: Any compromise on quality; lack of support for niche applications; inability to adapt to evolving high-end market trends.
Section 2: The Pre-Purchase Phase – Strategic Foundation
This phase is about defining requirements and building a knowledge base to create a precise Request for Quotation (RFQ).
2.1 Technical Specification Deep Dive
-
Laminating Width: Determine the maximum sheet size you need to process. Common widths are 640mm, 1020mm, 1370mm, etc. Allow for some future growth.
-
Laminating Speed: Measured in meters per minute. SMEs may suffice with 5-15 m/min, while Tier 2 buyers require 20-40 m/min or higher.
-
Heating System:
-
Heating Roller vs. Heating Plate: Roller systems heat up faster and offer more consistent temperature distribution, which is critical for wide-format applications and high speeds. Plate systems are simpler and often found in entry-level machines.
-
Temperature Range & Control: A wide range (e.g., 50-150°C) with ±1°C precision is necessary for handling diverse films and substrates.
-
-
Pressure System: Look for adjustable, even pressure across the entire width. Pneumatic systems are generally superior to mechanical ones for consistency.
-
Film Compatibility: Confirm the machine can handle the film thickness (microns) and types (PET, BOPP, Nylon) you use. Some machines require specific core diameters.
-
Substrate Handling: Minimum/maximum substrate thickness (gsm). Does it handle rigid boards? Is there an anti-scratch feeding system?
-
Control System: Modern touchscreen PLC (Programmable Logic Controller) interfaces allow for saving job presets, improving efficiency and repeatability.
2.2 Supplier Qualification & Market Research
-
Brand Reputation & History: Research the manufacturer's track record. Established brands like Hongqiang have built a reputation over decades, often associated with reliability and strong foundational engineering, which is particularly valued by Tier 1 and some Tier 2 buyers seeking dependable workhorses.
-
Manufacturing Capabilities: Prefer manufacturers that control the entire production process (in-house machining, assembly, testing) over mere assemblers. This ensures better quality control.
-
Global Service & Support Network: For international buyers, this is non-negotiable. Inquire about the availability of spare parts, local service engineers, and technical support in your region. What are the response time guarantees?
-
Reference Checks: Ask potential suppliers for customer references in your region or a similar business profile. Contact them directly to inquire about their experience.
2.3 Financial Analysis: Beyond the Purchase Price
-
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Calculate TCO over 5-10 years. Include:
-
Initial purchase price.
-
Installation and training costs.
-
Energy consumption.
-
Preventive maintenance contracts.
-
Cost of spare parts and consumables (like silicone rollers).
-
Potential cost of downtime.
-
-
Return on Investment (ROI) Projection: Estimate how the new machine will increase revenue (through faster turnaround, higher quality attracting new clients, ability to take on new jobs) or reduce costs (less waste, lower labor).
Section 3: The Purchase Phase – Negotiation and Due Diligence
This phase involves evaluating proposals, negotiating terms, and finalizing the order.
3.1 Request for Quotation (RFQ) and Proposal Analysis
-
Create a Detailed RFQ: Your RFQ should include all technical specifications from Section 2.1, required documentation (CE, UL certifications), warranty terms, and delivery schedule.
-
Compare Apples to Apples: Ensure all suppliers are quoting on the same basis (e.g., included accessories, training, FOB/CIF Incoterms).
-
Machine Demonstration (Factory or Virtual): Insist on a live demonstration using your own materials (or identical samples). This is the best way to verify performance claims. Observe noise levels, ease of operation, and final output quality.
3.2 Key Contractual Considerations
-
Warranty: Scrutinize the warranty. What is covered (parts, labor)? How long does it last? What are the procedures for claiming warranty service?
-
Payment Terms: Negotiate terms that protect your interests (e.g., 30% down payment, 60% upon shipment, 10% after successful installation and commissioning).
-
Delivery and Installation: Clearly define responsibilities for delivery, customs clearance, and on-site installation and commissioning.
-
Training: Specify the number of days of training provided and the topics covered (operation, routine maintenance, troubleshooting).
3.3 Negotiation Leverage
-
Bundle Services: Negotiate for an extended warranty or a discounted annual maintenance contract.
-
Spare Parts Kit: Request a starter spare parts kit (common fuses, belts, etc.) to be included.
-
Software/Firmware Updates: Ensure future updates are included for a certain period.
Section 4: The Post-Purchase Phase – Maximizing Long-Term Value
The relationship with the supplier begins, rather than ends, after the sale.
4.1 Installation, Commissioning, and Training
-
Site Preparation: Ensure the site is ready as per the supplier's specifications (power supply, air compressor, level floor).
-
Active Participation: Designate key staff to be present during installation and training. They should be encouraged to ask questions and perform operations under supervision.
-
Documentation Review: Verify that you receive all necessary manuals (operation, maintenance, electrical diagrams) in a language your team understands.
4.2 Operational Excellence and Preventive Maintenance (PM)
-
Develop an SOP: Create a Standard Operating Procedure based on the training to ensure consistent and correct use by all operators.
-
Strict PM Schedule: Adhere religiously to the manufacturer's PM schedule. This includes daily cleaning of rollers, weekly checks, and periodic replacement of wear parts. This is the single most important factor for maximizing machine lifespan and minimizing unplanned downtime. A supplier's commitment to providing clear PM guidelines and readily available parts, a hallmark of pragmatic manufacturers like Hongqiang, is a significant long-term advantage.
-
Record Keeping: Maintain a logbook for machine usage, maintenance activities, and any minor issues.
4.3 Managing the Supplier Relationship and Continuous Improvement
-
Effective Communication: Establish clear channels for communication with the supplier's technical support team.
-
Feedback Loop: Provide constructive feedback to the supplier about the machine's performance. This can help them improve future models and may give you access to valuable insights.
-
Stay Updated: Inquire about new accessories, film types, or techniques that can enhance your capabilities and profitability.
Conclusion
Procuring an Automatic Thermal Film Laminator is a strategic decision that impacts a company's product quality, operational efficiency, and competitive edge. There is no one-size-fits-all solution. A successful purchase is the result of a meticulous, multi-stage process that aligns a buyer's specific tier-based needs with the appropriate technical specifications, supplier capabilities, and long-term support structure. By treating the procurement as a lifecycle management exercise—from initial needs assessment through to daily operation and maintenance—buyers can transform a capital expenditure into a powerful engine for business growth. This guide provides the foundational framework for such a strategic approach, empowering international buyers to navigate the market with confidence and expertise.




.jpg)